Typing DOS commands on the Windows Command Line prompt is a most efficient and faster way of doing things in Windows XP. Here’s a run-down of the most useful DOS commands available in Windows XP. Some of these DOS commands even do not have an visual alternative.
DOS Command-line tools must be run at the prompt of the Cmd.exe command interpreter. To open Command Prompt, click Start, click Run, type cmd, and then click OK.
ipconfig – Windows IP configuration
Useful for troubleshooting your internet connection. Displays the current IP address of your computer and the DNS server address. If you call your ISP for reporting a bad internet connection, he will probably ask you to run ipconfig.
fc – Free BeyondCompare in XP
FC is an advanced DOS Command that compares two files and displays the differences between them. Though the file comparison results are not as interactive as BeyondCompare or Altova DiffDog, fc is still very useful. You can even set fc to resynchronize the files after finding a mismatch.
type – open text files sans Notepad
Similar to Unix cat command, Type is my favorite DOS command for displaying the contents of a text files without modifying them. When used in combination with more switch, type splits the contents of lengthy text files into multiple pages. Avoid using the type command with binary files or you’ll hear alien PC beeps and see some greek characters on your PC.
ping – Say hello to another computer
Ping network command followed by the web-address or IP address tells you about the health of the connection and whether the other party is responding to your handshake request. Ping tool can also be used to convert the web address to a physical IP address.
tree – visual directory structure
You often need to take prints of your physical directory structure but XP has no simple “visual” commands for printing directory contents. Here, try the Tree DOS command and redirect the output to a text file.
tree > mydirectory.txt
print mydirectory.txt
attrib – make hidden files visible
Attrib lets you change attributes of System files and even hidden files. This is great for troubleshooting Windows XP. Say your XP doesn’t boot ever since you edited that startup boot.ini file (Hidden), use attrib to remove the Hidden attibute and edit the file using EDIT dos command.
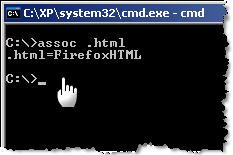
assoc – which program will open that .xyz file
The assoc DOS command can be used to either isplay or even modify the file name extension associations. The command assoc .htm will quickly tell you the name of your default web browser (see picture)
move – more flexible than copy-paste
Say you got a lot of XLS and DOC files in you MyDocuments folder and want to move only those XLS files that have their name ending with 2006. In XP Explorer, you have to manually select each file and then cut-paste to another folder. However, the DOS move command make things much simpler. Just type the following at the command prompt:
move *2006.xls c:2006Reports
find – advanced file search with filter
Find is the most powerful DOS command and even more useful than the Windows Desktop Search tool or the Windows Find Wizard. The find command searches for a specific string of text in a file or files. After searching the specified file or files, find displays any lines of text that contain the specified string.
To search your hard disk to find and display the file names on drive C: that contain the string “Google” use the pipe (|) to direct the results of a dir command to find as follows:
dir c: /s /b | find “Google”
Quick tip – Drag to avoid typing: When your command acts on a file or folder, you must type the path to that folder after the command. You can save typing time by dragging the file or folder from Windows Explorer into the command window.
To view help at the command-line, at the command prompt, type the following:
CommandName /?